Globally, there are several vaccines that are either approved or have received emergency authorisation based on preliminary evidence that they are safe and effective
THERE are at least 65 Covid-19 vaccines currently in clinical trials and 20 have reached the final stages of testing.
Before vaccines are approved, they have to meet the must-have criteria for safety and efficacy set out by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Globally, there are several vaccines that are either approved or have received emergency authorisation based on preliminary evidence that they are safe and effective.
So, what are the different vaccines currently available and how do they work?
How do Covid-19 vaccines work?
Covid-19 vaccines help our bodies develop immunity to the virus that causes Covid-19 without us having to get the illness. Different types of vaccines work in different ways to offer protection.
Types of vaccines
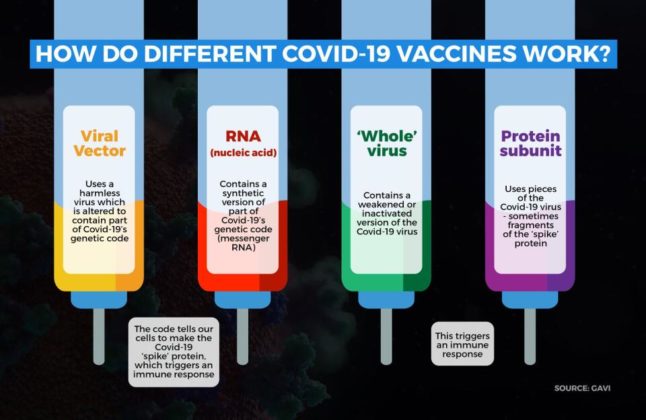
The Covid-19 vaccines that are currently the most advanced are using four different approaches:
Viral vector: They differ from most conventional vaccines in that they don’t actually contain antigens, but rather use the body’s own cells to produce them. There are two main types of viral vector-based vaccines. Non-replicating vector vaccines are unable to make new viral particles; they only produce the vaccine antigen.
mRNA: These vaccines are a new type of vaccine to protect against infectious diseases. They teach our cells how to make a protein — or even just a piece of a protein — that triggers an immune response inside our bodies.
Protein subunit: They are made using living organisms, such as bacteria and yeast, which require substrates on which to grow them, and strict hygiene to avoid contamination with other organisms. This makes them more expensive to produce than chemically-synthesised vaccines, such as RNA vaccines.
Whole virus: They use a weakened (attenuated) or deactivated form of the pathogen that causes a disease to trigger protective immunity to it. The first human vaccines against viruses were based using weaker or attenuated viruses to generate immunity. Rabies was the first virus attenuated in a lab to create a vaccine for humans.
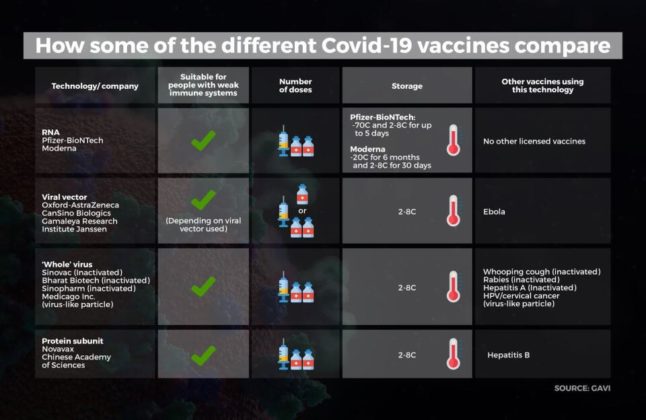
Covid-19 vaccines currently in use
1.Oxford–AstraZeneca
The vaccine developed by Oxford University and AstraZeneca.
Vaccine name: AZD1222 (also known as Covishield in India)
Efficacy: 62% to 90%, depending on dosage
Dose: 2 doses, 4 weeks apart
Type: Viral vector
Storage: Stable in refrigerator for at least 6 months
2. Moderna vaccine
The vaccine is developed by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), and Moderna.
Vaccine name: mRNA-1273
Efficacy: 94.5%
Dose: 2 doses, 4 weeks apart
Type: mRNA
Storage: 30 days with refrigeration, 6 months at –4°F (–20°C)
3. Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine
The vaccine is developed by BioNtech in co-operation with Pfizer.
Vaccine name: Comirnaty (also known as tozinameran or BNT162b2)
Efficacy: 95%
Dose: 2 doses, 3 weeks apart
Type: mRNA
Storage: Freezer storage only at –94°F (–70°C)
4.The Sputnik V
It is a Covid-19 vaccine developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology.
Vaccine name: Sputnik V (also known as Gam-Covid-Vac)
Efficacy: 91.4%
Dose: 2 doses, 3 weeks apart
Type: Viral Vector
Storage: Freezer storage. Developing an alternative formulation that can be refrigerated.
5. BBIBP-CorV
The vaccine was created by the Beijing Institute of Biological Products and put into clinical trials by the state-owned Chinese company Sinopharm. Egypt and Jordan gave it emergency authorisation in January.
Vaccine name: BBIBP-CorV
Efficacy: 79.34%
Dose: 2 doses, 3 weeks apart
Type: inactivated whole virus
6. CoronaVac
The vaccine was developed by Chinese private company Sinovac Biotech. It was included in the Chinese emergency vaccination programme.
Vaccine name: CoronaVac (formerly PiCoVacc)
Efficacy: Less than 78 percent
Dose: 2 doses, 2 weeks apart
Type: inactivated whole virus
Storage: Refrigerated
Common side effects
On the arm where you got the shot:
– Pain
– Swelling
Throughout the rest of your body:
– Fever
– Chills
– Tiredness
– Headache
It’s quite common to develop a fever after a vaccination. This normally happens within 48 hours of the vaccination and usually goes away within 48 hours.
A less common side effect is swelling of the glands, which could start a few days after the vaccine and may last for up to two weeks. This is to be expected and is a sign of the immune system responding to the vaccine.